JAVA_HOME、PATH與CLASSPATH是與開發Java程式緊緊相關的環境變數。以下介紹為何要設定它們。
JAVA_HOME: JAVA所在目錄,設定此環境變數提供Eclipse、NetBeans等軟體找到安裝好的SDK。
PATH: 在命令模式下欲透過javac進行編譯或者java執行程式,需告訴系統要到哪個目錄尋找javac與java等工具,此時就是透過設定PATH環境變數,讓系統知道到哪裡尋找這些工具。JDK將工具程式放在bin目錄下,因此要將 C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_25\bin 加入PATH環境變數中。
CLASSPATH: 設定class尋找路徑,供JVM尋找class。在C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_25\lib 下有dt.jar與tools.jar等類別打包過後的壓縮檔。
註: jar (JAVA Archive) 是一種資料格式,可將數個class集合在一個壓縮檔。它是建構在Zip之上,所以用解Zip的工具去解壓縮它也是可以的。
[Java筆記][草稿] 字串物件
字串是包裹字元陣列的物件,是java.lang.String類別的實例
字串建立方法1 - 使用 " " 包括一串字元來建立字串 Ex:
String name = "Lupin"
因為字串是java.lang.String的實例,所以可以透過很多方法來操作這個物件
name.length() //顯示字串長度
name.charAt(0) //顯示第一個字元
name.toUpperCase() //將字串轉為大寫
字串建立方法2 - 如果已經有字元陣列,可以使用new來建構String實例,例如
char[] cs = {'L','u','p','i','n'};
String name = new String(cs);
若要將字串傳入char[]陣列,可以使用 toCharArray();
char[] cs2 = name.toCharArray();
使用 + 可以串接字串,Ex
System.out.println("Your name is: " + name);
將字串剖析為基本型態
Byte.parseByte(number) //將number 剖析為byte整數
Short.parseShort(number) //將number剖析為short整數
Integer.parseInt(number)
Long.parseLong(number)
Float.parseFloat(number)
Double.parseDouble(number)
字串建立方法1 - 使用 " " 包括一串字元來建立字串 Ex:
String name = "Lupin"
因為字串是java.lang.String的實例,所以可以透過很多方法來操作這個物件
name.length() //顯示字串長度
name.charAt(0) //顯示第一個字元
name.toUpperCase() //將字串轉為大寫
字串建立方法2 - 如果已經有字元陣列,可以使用new來建構String實例,例如
char[] cs = {'L','u','p','i','n'};
String name = new String(cs);
若要將字串傳入char[]陣列,可以使用 toCharArray();
char[] cs2 = name.toCharArray();
使用 + 可以串接字串,Ex
System.out.println("Your name is: " + name);
將字串剖析為基本型態
Byte.parseByte(number) //將number 剖析為byte整數
Short.parseShort(number) //將number剖析為short整數
Integer.parseInt(number)
Long.parseLong(number)
Float.parseFloat(number)
Double.parseDouble(number)
[Java] Primitive type 基本型態的長度
Java 的型態分為 Primitive type 基本型態與 Class type 類別型態
基本型態分為
整數
short 2位元組
int 4位元組
long 8位元組
位元組
1位元組,可表示 -128到127的整數
浮點數
float 4位元組
double 8位元組
字元
char 2位元組
布林
true/false
基本型態分為
整數
short 2位元組
int 4位元組
long 8位元組
位元組
1位元組,可表示 -128到127的整數
浮點數
float 4位元組
double 8位元組
字元
char 2位元組
布林
true/false
Java 編譯器 Javac 參數列表
-sourcepath 告訴編譯器原始碼所在位置
-d 指定編譯完成的位元碼(.class) 存放的資料夾
-verbose 輸出編譯的過程
-classpath 告訴編譯器到何處尋找先前已編譯好的位元碼存放位置
-source 檢查使用語法是否有超過指定的版本號
-target 指定編譯出來的位元碼,符合指定平台允許的版本號 (-target 必須大於等於 -source)
-bootstrap 指定類別載入器,搭配source與target使用,類別載入器會參考到rt.jar,可避免因為舊版JRE沒有新API造成無法執行的情形。
-version 執行版本資訊
範例
javac -sourcepath src -d classes src/Main.java
說明
使用java編譯器javac,編譯src/Main.java,到sourcepath指定的src目錄下尋找有用到原始檔,編譯完畢將檔案放置在classes目錄下
完整參數列表
Usage: javac <options> <source files>
where possible options include:
-g Generate all debugging info
-g:none Generate no debugging info
-g:{lines,vars,source} Generate only some debugging info
-nowarn Generate no warnings
-verbose Output messages about what the compiler is doing
-deprecation Output source locations where deprecated APIs are u
sed
-classpath <path> Specify where to find user class files and annotati
on processors
-cp <path> Specify where to find user class files and annotati
on processors
-sourcepath <path> Specify where to find input source files
-bootclasspath <path> Override location of bootstrap class files
-extdirs <dirs> Override location of installed extensions
-endorseddirs <dirs> Override location of endorsed standards path
-proc:{none,only} Control whether annotation processing and/or compil
ation is done.
-processor <class1>[,<class2>,<class3>...] Names of the annotation processors
to run; bypasses default discovery process
-processorpath <path> Specify where to find annotation processors
-parameters Generate metadata for reflection on method paramete
rs
-d <directory> Specify where to place generated class files
-s <directory> Specify where to place generated source files
-h <directory> Specify where to place generated native header file
s
-implicit:{none,class} Specify whether or not to generate class files for
implicitly referenced files
-encoding <encoding> Specify character encoding used by source files
-source <release> Provide source compatibility with specified release
-target <release> Generate class files for specific VM version
-profile <profile> Check that API used is available in the specified p
rofile
-version Version information
-help Print a synopsis of standard options
-Akey[=value] Options to pass to annotation processors
-X Print a synopsis of nonstandard options
-J<flag> Pass <flag> directly to the runtime system
-Werror Terminate compilation if warnings occur
@<filename> Read options and filenames from file
-d 指定編譯完成的位元碼(.class) 存放的資料夾
-verbose 輸出編譯的過程
-classpath 告訴編譯器到何處尋找先前已編譯好的位元碼存放位置
-source 檢查使用語法是否有超過指定的版本號
-target 指定編譯出來的位元碼,符合指定平台允許的版本號 (-target 必須大於等於 -source)
-bootstrap 指定類別載入器,搭配source與target使用,類別載入器會參考到rt.jar,可避免因為舊版JRE沒有新API造成無法執行的情形。
-version 執行版本資訊
範例
javac -sourcepath src -d classes src/Main.java
說明
使用java編譯器javac,編譯src/Main.java,到sourcepath指定的src目錄下尋找有用到原始檔,編譯完畢將檔案放置在classes目錄下
完整參數列表
Usage: javac <options> <source files>
where possible options include:
-g Generate all debugging info
-g:none Generate no debugging info
-g:{lines,vars,source} Generate only some debugging info
-nowarn Generate no warnings
-verbose Output messages about what the compiler is doing
-deprecation Output source locations where deprecated APIs are u
sed
-classpath <path> Specify where to find user class files and annotati
on processors
-cp <path> Specify where to find user class files and annotati
on processors
-sourcepath <path> Specify where to find input source files
-bootclasspath <path> Override location of bootstrap class files
-extdirs <dirs> Override location of installed extensions
-endorseddirs <dirs> Override location of endorsed standards path
-proc:{none,only} Control whether annotation processing and/or compil
ation is done.
-processor <class1>[,<class2>,<class3>...] Names of the annotation processors
to run; bypasses default discovery process
-processorpath <path> Specify where to find annotation processors
-parameters Generate metadata for reflection on method paramete
rs
-d <directory> Specify where to place generated class files
-s <directory> Specify where to place generated source files
-h <directory> Specify where to place generated native header file
s
-implicit:{none,class} Specify whether or not to generate class files for
implicitly referenced files
-encoding <encoding> Specify character encoding used by source files
-source <release> Provide source compatibility with specified release
-target <release> Generate class files for specific VM version
-profile <profile> Check that API used is available in the specified p
rofile
-version Version information
-help Print a synopsis of standard options
-Akey[=value] Options to pass to annotation processors
-X Print a synopsis of nonstandard options
-J<flag> Pass <flag> directly to the runtime system
-Werror Terminate compilation if warnings occur
@<filename> Read options and filenames from file
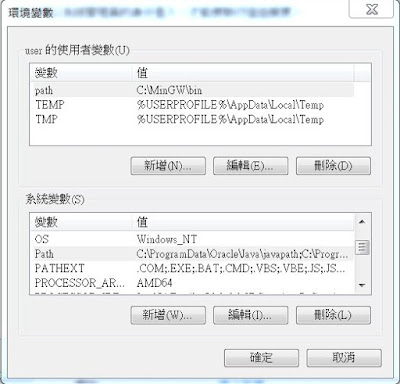
查詢PATH環境變數
想要查詢目前Windows的PATH環境變數,可以透過 echo %PATH% 進行查詢
使用 SET PATH = 路徑 可以設定PATH環境變數,但視窗關閉後設定就失效了。下例: SET PATH = C:\JAVA\bin;%PATH%,新增C:\JAVA\bin這個路徑到環境變數中,多個路徑會使用分號(;) 進行區隔。此範例透過分號將新路徑(C:\JAVA\bin)和舊路徑(%PATH%)結合在一起。
每次都要設定環境變數很麻煩,此時可設定系統環境變數。
設定方式: 開始 > 電腦 > 點擊右鍵 > 內容 > 進階系統設定 > 環境變數 > 在User的使用變數(U) 或系統變數(S) 中找到Path > 點擊編輯(I)... 或新增(N)... 便可以將要新增的路徑加入Path中。
註: 由於Path的尋找是循序漸進,最前方的Path最先採用。因此,新的Path建議加在前方,才會執行到你想要的工具程式。
使用 SET PATH = 路徑 可以設定PATH環境變數,但視窗關閉後設定就失效了。下例: SET PATH = C:\JAVA\bin;%PATH%,新增C:\JAVA\bin這個路徑到環境變數中,多個路徑會使用分號(;) 進行區隔。此範例透過分號將新路徑(C:\JAVA\bin)和舊路徑(%PATH%)結合在一起。
每次都要設定環境變數很麻煩,此時可設定系統環境變數。
設定方式: 開始 > 電腦 > 點擊右鍵 > 內容 > 進階系統設定 > 環境變數 > 在User的使用變數(U) 或系統變數(S) 中找到Path > 點擊編輯(I)... 或新增(N)... 便可以將要新增的路徑加入Path中。
註: 由於Path的尋找是循序漸進,最前方的Path最先採用。因此,新的Path建議加在前方,才會執行到你想要的工具程式。
[Java] 字串比較Method compareTo
compareTo 可用來比較兩字串是否相同,它屬於 Class String。當回傳值為0時,表示兩字串相等。
範例
String string1;
String string2;
if (string1.compareTo(string2) == 0)
兩字串相等
else
兩字串不相等
compareTo
public int compareTo(String anotherString)
Compares two strings lexicographically. The comparison is based on the Unicode value of each character in the strings. The character sequence represented by thisStringobject is compared lexicographically to the character sequence represented by the argument string. The result is a negative integer if thisStringobject lexicographically precedes the argument string. The result is a positive integer if thisStringobject lexicographically follows the argument string. The result is zero if the strings are equal;compareToreturns0exactly when theequals(Object)method would returntrue.This is the definition of lexicographic ordering. If two strings are different, then either they have different characters at some index that is a valid index for both strings, or their lengths are different, or both. If they have different characters at one or more index positions, let k be the smallest such index; then the string whose character at position k has the smaller value, as determined by using the < operator, lexicographically precedes the other string. In this case,compareToreturns the difference of the two character values at positionkin the two string -- that is, the value:
If there is no index position at which they differ, then the shorter string lexicographically precedes the longer string. In this case,this.charAt(k)-anotherString.charAt(k)
compareToreturns the difference of the lengths of the strings -- that is, the value:this.length()-anotherString.length()
- Specified by:
compareToin interfaceComparable<String>- Parameters:
anotherString- theStringto be compared.- Returns:
- the value
0if the argument string is equal to this string; a value less than0if this string is lexicographically less than the string argument; and a value greater than0if this string is lexicographically greater than the string argument.
Android Studio 設定 Font Size 的方法
Android Studio設定Font Size的方法
設定Font Size路徑
1. File > Settings (Crtl+Alt+S)
2. IDE Settings > Editor > Colors & Fonts > Font
3. 點選 Save As...,輸入新的Scheme name,輸入完畢,點選OK
4. 修改Size欄位數值
5. 點選OK完成修改
設定Font Size路徑
1. File > Settings (Crtl+Alt+S)
2. IDE Settings > Editor > Colors & Fonts > Font
3. 點選 Save As...,輸入新的Scheme name,輸入完畢,點選OK
4. 修改Size欄位數值
5. 點選OK完成修改
清華大學 計算機網路 期末考
| (+5) | 【 單選題 】
(5%) 1. Which of the following statements are correct for delivering packets (datagrams) over the Internet ?
| |
| (a) All packets destined to the same destination will be forwarded along the same routing path. | ||
| (b) The routing path of a packet is determined first before the packet is sending into the Internet. | ||
| (c) The Internet is reliable so that all packets will be received by the destination correctly. | ||
| (d) A packet may be partitioned into several fragments by routers. | ||
| (e) All fragments of a packet will be forwarded along the same path to the destination. | ||
| (+5) | 【 複選題 】
(5%)2. Which of the following statements are correct for “statistical multiplexing” ?
| |
| (a) Data are transmitted based on demand of each flow. | ||
| (b) Data are transmitted based on the arrival time of each flow. | ||
| (c) The bandwidth used by different flows may be different. | ||
| (d)The statistical multiplexing is fair due to the bandwidth used by different flows are the same. | ||
| (e)It provides better link utilization than TDM (Time-Division-Multiplexing) and FDM (Frequency-Division- Multiplexing). | ||
| (+5) | 【 複選題 】
(5%) 3. Which of the following are correct for CSMA/CD (Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection) protocol ?
| |
| (a)Listen (carrier sense) before transmit. | ||
| (b)If channel is sensed idle, then transmit entire frame without considering if frame collision is detected. | ||
| (c)If channel is sensed idle, then transmit a frame and stop the transmission when a collision is detected. | ||
| (d)If channel is sensed busy, then defer transmission until the channel is idle. | ||
| (e)If channel is sensed busy, then defer transmission for a random time. | ||
| (+5) | 【 複選題 】
(5%) 4. The “collision window” of the CSMA/CD protocol is time required to detect a collision. Which of the following are correct for collision window ? Assume the one way propagation time of the network is “a”
| |
| (a)The collision window is equal to a | ||
| (b)The collision window is equal to 2a | ||
| (c)The worst case scenario happens when the two hosts are at opposite ends of the Ethernet | ||
| (d)The best case scenario happens when the two hosts are close to each other. | ||
| (e)The worst case scenario happens when the two hosts are close to each other. | ||
| (+5) | 【 複選題 】
(5%) 5. What are the purposes of RTS and CTS control frames used in IEEE 802.11 wireless LAN ?
| |
| (a)Reserve the wireless channel for a time period | ||
| (b)Informs all nearby nodes that a transmission is about to begin | ||
| (c)These two frames also contain data to transmit. | ||
| (d)The sender is asking the receiver to send back a frame after a time period | ||
| (e)The duration field in the RTS and CTS frames is used to specify the time period needs to transmit the frame | ||
| (+5) | 【 複選題 】
(5%) 6. Which of the following statements about the CSMA/CA are correct ?
| |
| (a)A station with a pending MPDU may transmit immediately when it detects the medium is free. | ||
| (b)A station with a pending MPDU may transmit when it detects a free medium for greater than or equal to a DIFS time. | ||
| (c)If the medium is busy when a station desires to transmit an MPDU, the station can transmit the MPDU when it detects a free medium for greater than or equal to a DIFS time. | ||
| (d)In CSMA/CA protocol, no packet collision will happen as the “collision avoidance” mechanism is used. | ||
| (e)If the medium is busy when a station desires to transmit an MPDU, the Random Backoff Time algorithm shall be followed after it detects a free medium for greater than or equal to a DIFS time. | ||
| (+5) | 【 複選題 】
(5%) 7. Consider the procedure to maintain the spanning tree of IEEE 802.1D spanning tree algorithm. For a bridge B with three ports x,y,z and root bridge ID = w, rpc = p. Assume port x is an R port, port y is a D port, port z is blocked and connected to a LAN M. Also assume port z has a transmission cost of c. What actions will be taken by the bridge B if the hello BPDUs suppose to be periodically received from port z are lost for a long time (a timeout event) ?
| |
| (a) Port z is selected as a new R port. | ||
| (b) Port z is selected as a D port. | ||
| (c) A BPDU (with root bridge ID = w, rpc =p) is forwarded to port z | ||
| (d) A BPDU (with root bridge ID = w, rpc = p+c) is forwarded to port z. | ||
| (e) A BPDU (with root bridge ID = w, rpc =p) is forwarded to port y. | ||
| (+5) | 【 複選題 】
(5%) 8. Consider the procedure to construct the spanning tree. When a bridge B (with root bridge ID = w, rpc = p) receives a BPDU (with root bridge ID = m, rpc =q) from port x (with a transmission cost of c). Assume w > m. Then what actions will be taken by bridge B ?
| |
| (a) port x will be selected as a new D port. | ||
| (b) port x will be selected as a new R port. | ||
| (c) A BPDU (with root bridge ID = m, rpc =q) will be forwarded to all the ports, except port x. | ||
| (d) A BPDU (with root bridge ID = w, rpc =q+c) will be forwarded to all the ports, except port x. | ||
| (e) A BPDU (with root bridge ID = m, rpc =q+c) will be forwarded to all the ports, except port x. | ||
| (+4) | 【 複選題 】
(4%) 9. Which of the following tagging rules for a “hybrid link” are correct ?
| |
| (a)For each VLAN, all frames traversing a particular hybrid link can be tagged in different ways. | ||
| (b)For each VLAN, all frames traversing a particular hybrid link must be tagged the same way: all implicitly tagged or all carrying the same explicit tag. | ||
| (c)There can be a mix of implicitly and explicit tagged frames but they must be for different VLANs. | ||
| (d)All the frames must be tagged explicitly. | ||
| (e)A frame traversing a particular hybrid will be tagged or untagged depends on which VLAN the frame came from. | ||
| (+6) | 【 填充題 】
(6%) 10. Consider the following VLAN configuration. For switch 1, what are the “member set” and “untagged set” of each VLAN ? please answer the port “number” for each of the following questions.
注意:在每一個VLAN中的答案請依數字大小排序,答案請由"," 隔開,並且答案欄裡不要輸入任何空白字元(答案後面也不要有空白)
EX:若A空格答案有4 2 1 3,請填入:1,2,3,4(注意逗號是英文輸入法的逗號,若不確定請直接複製 ",")
Member set:
VLAN1:__A__
VLAN2:__B__
VLAN3:__C__
Untagged set:
VLAN1:__D__
VLAN2:__E__
VLAN3:__F__
| |
| A= | ANS:2,3,4,5 | |
| B= | ANS:7,11,12 | |
| C= | ANS:6,7,8,9 | |
| D= | ANS:2,3,4,5 | |
| E= | ANS:11,12 | |
| F= | ANS:8,9 | |
| (+5) | 【 複選題 】
(5%)11. Let SeqNumToAck denote the largest sequence number not yet acknowledged, such that all frames with sequence number less than SeqNumToAck have been received. Which of the following statements are correct for the “cumulative acknowledgement” ?
| |
| (a)The receiver acknowledges SeqNumToAck+k to sender if a frame with sequence number of SeqNumToAck + k, k > 0, is received. | ||
| (b)The receiver acknowledges SeqNumToAck to sender if a frame with sequence number of SeqNumToAck + k, k > 0, is received. | ||
| (c)The receiver then sets LFR = SeqNumToAck + 1 and LAF = LFR + RWS-1. | ||
| (d)The receiver then sets LFR = SeqNumToAck and LAF = LFR + RWS. | ||
| (e)The receiver then sets LFR = SeqNumToAck - 1 and LAF = LFR + RWS. | ||
| (+5) | 【 單選題 】
(5%)12. Let MaxSeqNum be the total number of available sequence numbers. Assume RWS = SWS, then which of the following relationship is sufficient to distinguish between different frames of the same sequence number ?
| |
| (a)SWS + 1 ≤ MaxSeqNum | ||
| (b)SWS ≤ (MaxSeqNum+1)/2 | ||
| (c)SWS = (MaxSeqNum+1)/2 | ||
| (d)SWS < MaxSeqNum x 2 | ||
| (e)SWS < (MaxSeqNum+1)/2 | ||
| (+6) | 【 填充題 】
(6%)13. With the CIDR, what is the “prefix” for all the networks 192.4.16 through 192.4.31 ? Assume the prefix is represented as 192.4.a/b, and therefore
a = _______A_______
b = _______B_______
| |
| A= | ANS:16 | |
| B= | ANS:20 | |
| (+4) | 【 複選題 】
(4%)14. Which of the following statements are correct for “Link State” routing protocol ? Assume that each node knows the cost of the link to each of its directly connected neighbors.
| |
| (a)Each node constructs a one dimensional array (a vector) containing the “distances” (costs) to all other nodes and distributes that vector to its immediate neighbors. | ||
| (b)Each node constructs a one dimensional array (a vector) containing the “distances” (costs) to all other nodes and distributes that vector to all other nodes. | ||
| (c)Each node constructs a one dimensional array (a vector) containing the “distances” (costs) to its immediate neighbors and distributes that vector to its immediate neighbors. | ||
| (d)Each node constructs a one dimensional array (a vector) containing the “distances” (costs) to its immediate neighbors and distributes that vector to all other nodes. | ||
| (e)The link state packets (LSP) are sent to all other nodes by using reliable flooding algorithm. | ||
| (+5) | 【 複選題 】
(5%)15. Which of the following statements are correct for “flow control and congestion control” ?
| |
| (a)Flow control involves preventing senders from overrunning the capacity of the receivers | ||
| (b)Flow control involves preventing senders from overrunning the capacity of the networks. | ||
| (c)Congestion control involves preventing senders from overrunning the capacity of the networks. | ||
| (d)Congestion control involves preventing senders from overrunning the capacity of the receivers. | ||
| (e)Congestion control involves preventing senders from overrunning the capacity of the receivers and networks. | ||
| (+5) | 【 單選題 】
(5%) 16. For the Additive Increase Multiplicative Decrease (AIMD) mechanism used in TCP congestion control, TCP does not wait for an entire window’s worth of ACKs to add 1 packet’s worth to the congestion window, but instead increments CongestionWindow by a little (denoted as increment) for each ACK. Which of the following is correct for this increment ?
| |
| (a) Increment =1/CongestionWindow | ||
| (b) Increment = 1/MSS | ||
| (c) Increment = MSS/CongestionWindow | ||
| (d) Increment = MSS (MSS/CongestionWindow) | ||
| (e) Increment = MSS/(CongestionWindow+MSS); | ||
| (+5) | 【 複選題 】
(5%) 17. Which of the following statements are correct for “slow start” in TCP congestion control ?
| |
| (a) Slow start effectively increases the congestion window linearly | ||
| (b) Slow start is used to increase the congestion window rapidly from a cold start | ||
| (c) When the ACK for a packet arrives TCP source, the TCP source adds 1 packet size of MSS to CongestionWindow | ||
| (d) When the ACK for a packet arrives TCP source, the TCP source doubles the size of CongestionWindow | ||
| (e) Slow start effectively doubles the number of packets the TCP source has in transit every RTT | ||
| (+5) | 【 複選題 】
(5%) 18. Which of the following statements are correct for a TCP source to handle the “packet lost” in congestion control ?
| |
| (a) After receives 3 duplicate ACKs, the CongestionWindow is cut in half and then grows linearly. | ||
| (b) After receives 3 duplicate ACKs, the CongestionWindow is set to 1 MSS and then grows linearly. | ||
| (c) After timeout event happes, the CongestionWindow is set to 1 MSS; the window then grows exponentially to a threshold, and then grows linearly. | ||
| (d) After timeout event happes, the CongestionWindow is set to 1 MSS; the window then grows linearly. | ||
| (e) After timeout event happes, the CongestionWindow is cut in half; the window then grows exponentially to a threshold, and then grows linearly. | ||
| (+10) | 【 填充題 】
(10%) 19. Consider the following figure to demonstrate the growth of CongestionWindow size for different “packet lost” events in TCP congestion control. We can use the following events to “describe” the curve in this figure. Initially, the connection is in slow start period with CongestionWindow size = 1 (1MSS).
Event 1: 3-duplicate ACKs happens at 5th RTT
Event 2: Timeout happens at 10th RTT
Event 3: 3-duplicate ACKs happens again at 18th RTT.
And we have a = 16 (window size), b = 8 (window size), c = 12 (window size), d = 6 (Threshold), e = 10 (window size), f = 5 (Threshold) as shown in the figure.
Now, consider we have the following events:
Event 1: 3-duplicate ACKs happens at 4th RTT
Event 2: Timeout happens at 17th RTT
Event 3: 3-duplicate ACKs happens again at 25th RTT.
Then we have
a = _____ (window size),
b = _____ (window size),
c = _____ (window size),
d = _____ (Threshold),
e = _____ (window size),
f = ______ (Threshold).
And what is the CongestionWindow size at the following points?
At 2nd RTT :__________g______
At 18th RTT :__________h_____
At 23th RTT :__________i______
At 29th RTT :__________j______
| |
| a= | ANS:8 | |
| b= | ANS:4 | |
| c= | ANS:16 | |
| d= | ANS:8 | |
| e= | ANS:12 | |
| f= | ANS:6 | |
| g= | ANS:2 | |
| h= | ANS:1 | |
| i= | ANS:10 | |
| j= | ANS:9 | |
訂閱:
意見 (Atom)